SQL Developer: A Complete Career Guide: A prominent SQL Developer does far more than just write queries. The developers architect, optimize, and secure the entire data layer of an database application.
SQL Developer: A Complete Career Guide:
With the larger amount of data that companies store today, database management has become all the more important. SQL developers—the tech professionals who build databases—have become key to these efforts, and are increasingly in demand.
What Does SQL Developer Do?
While specific works may vary, an SQL developer creates and maintains a database to suit the business requirements. They are familiar with a vast range of database system and software, including Oracle Microsoft and big query products.
Some tasks and works that an SQL developer performs are:
- An SQL developer is responsible for database systems design, which are used for storing and accessing business-related data and information.
- They are responsible for creating, manipulating, and truncating data as required by a particular application.
- An SQL developer makes informed decisions regarding suitable database languages and technologies.
- They work on evaluating the network infrastructure, running multiple diagnostic tests, and updating the information security systems for optimal performance and efficient navigation.
- They also document code, unit-testing, provide progress reports and analytics , and perform code review and peer feedback.
- They are also responsible for testing and checking code for bugs and implementing fixes.
- Another most important task or responsible work for a sql developer to optimize the query to retrieve the records from database very fast.
Key Technical Skills and Competencies of SQL Developer:
1. Advanced SQL Querying and knowledge on the advanced SQL clauses:
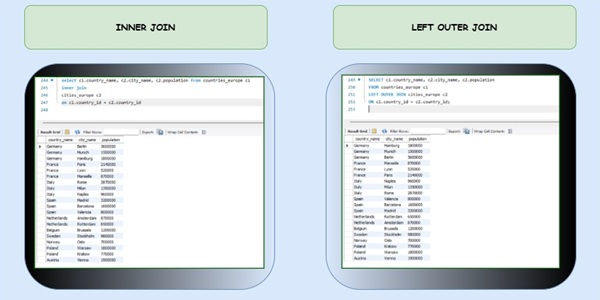
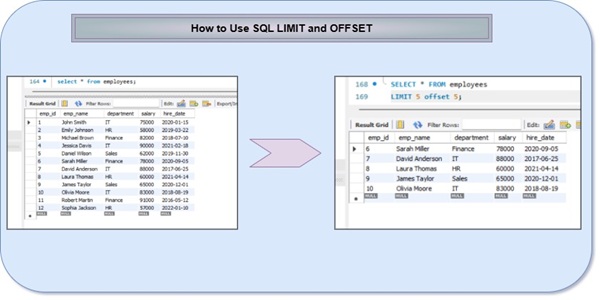
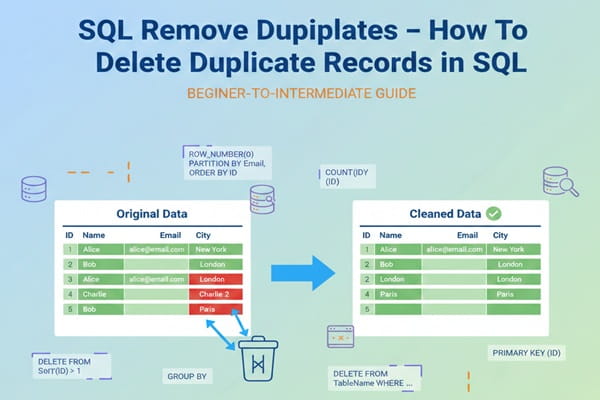
You should be able to write complex JOINs, nested subqueries, window functions, and common table expressions (CTEs) without blinking. This isn’t just about retrieving data, it’s about doing it efficiently and at scale. You’ll often need to write queries that work on millions of records without breaking performance, having small execution time.
2. Database Design and Normalization:
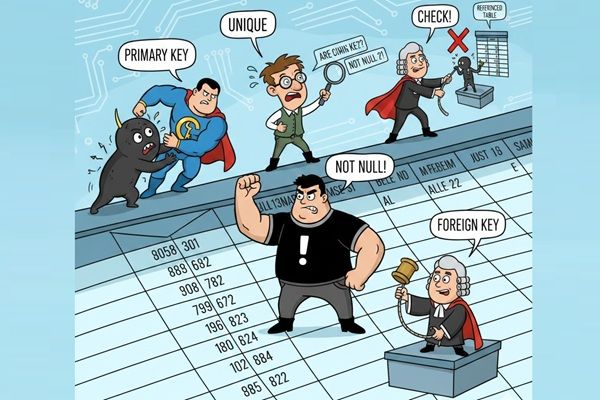
Understanding data modeling is fundamental for the database system works. You need to know how to structure databases using 3NF (Third Normal Form), when to denormalize for performance, and how to set up proper primary/foreign keys, indexes, stored procedure and constraints. Poor schema design causes chaos down the road—your job is to avoid it.
3. Performance Tuning and Optimization:
Slow and time taking queries kill applications. You’ll need hands-on skills with execution plans, indexing strategies, table partitioning, and query refactoring. Knowing how the optimizer thinks—and how to outsmart it when needed—is a must.
4. Stored Procedures, Functions, and Triggers:
You should be comfortable writing modular, reusable procedures in T-SQL, PL/SQL, or whatever flavor your DBMS uses. Triggers can automate validations or workflows, but using them well (and sparingly) takes real experience.
5. Data Integration & ETL:
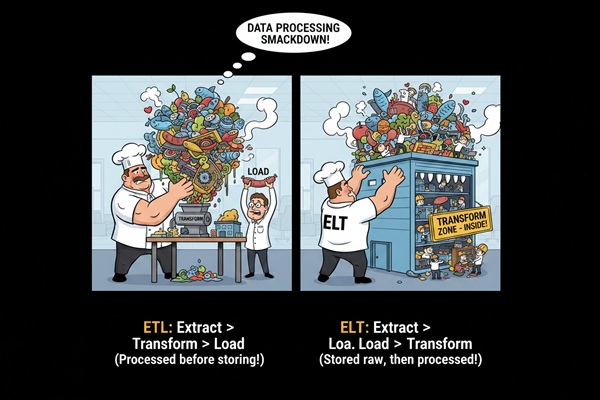
SQL Developers often manage data ingestion from multiple sources. You’ll work with ETL pipelines, big queries maybe use tools like Apache NiFi, Talend, or Python scripts, and handle data cleaning, deduplication, and transformations along the way.
6. Relational Database Engines:
You should have a deep working knowledge of at least one major RDBMS—SQL Server, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MySQL, or MariaDB. Knowing vendor-specific extensions and tuning techniques is key.
7. Transactions and Concurrency:
Data integrity matters. You need to understand ACID properties, isolation levels, locking mechanisms, deadlocks, and how to handle concurrent updates without corrupting your data.
8. Version Control and CI/CD:
You can’t just be writing scripts on your local machine. Knowing how to version your SQL code using Git, and maybe plug it into a CI/CD pipeline with Liquibase, Flyway, or similar tools, gives you a serious edge.
9. Basic Scripting for Automation:
You’ll often write Bash, PowerShell, or Python scripts to automate routine tasks, like backups, schema migrations, or scheduled reports.
10. Security and Access Control:
Know how to grant permissions, define roles, implement row-level security, and follow best practices for sensitive data handling. If a junior dev accidentally gets access to the prod database, you should’ve caught it before it happened.
SQL Developer Salary:
The salary for an SQL developer can vary widely based on factors such as experience, location, and industry. Understanding the average earnings for this role can help you gauge the financial prospects and set career expectations in the field of database management. Let’s learn in detail about the SQL developer salary in the USA.
SQL Developer Salary in the USA:
SQL developers can expect to earn competitive salaries in the US. The average total compensation, which includes tips, bonuses, and overtime pay, varies depending on experience level. Here’s a breakdown of SQL developer salaries in the US based on the work experience (Source: Payscale):
- Entry Level (Less than 1 year): $59,590 (based on 46 salaries)
- Early Career (1-4 years): $73,781 (based on 282 salaries)
- Mid-Career (5-9 years): $86,027 (based on 240 salaries)
- Experienced (10-19 years): $100,267 (based on 132 salaries)
- Late Career (20+ years): $110,488 (based on 132 salaries)
SQL Salary Comparisons by City
| City | Average Salary (per year) | Total Pay Range | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco, CA | $162,000 | $141K – $191K | Glassdoor |
| Seattle, WA | $131,000 | $114K – $153K | Glassdoor |
| New York City, NY | $134,000 | $107K – $167K | Indeed |
| Austin, TX | $95,000 | $87K – $107K | Glassdoor |
| Raleigh, NC | $99,000 | $93K – $106K | Indeed |
| Denver, CO | $113,000 | $101K – $129K | Glassdoor |
Top Paying Companies for SQL Developers:
| Company | Total Pay Range | Median Total Pay (per year) | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | $175K – $250K | $215,000 | Technology |
| $174K – $249K | $211,500 | Technology | |
| Microsoft | $153K – $210K | $181,500 | Technology |
| Wells Fargo | $156,655 | $156,655 | Financial Services |
| Bank of America | $140,795 | $140,795 | Financial Services |
| SEI Investments | $130,861 | $130,861 | Financial Services |
SQL Developer certification:
The certification is not mandatory to enter the workforce, some employers require their SQL developer candidates to have application-specific certifications. Examples of relevant and recommended professional certifications include:
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Database Administrator Associate
- Oracle Database SQL Certified Associate
- AWS Certified Database – Specialty
- Google Professional Data Engineer (includes SQL-heavy content)
- Databricks Data Engineer Associate (includes SQL for big data contexts)
You can become a certified SQL developer by passing the certification exam. Employers often prefer SQL developers to be experts in one system rather than having basic knowledge in several database environments.While certifications aren’t mandatory, they can help differentiate candidates, especially when targeting roles that work with specific technologies like Azure, AWS or Oracle.
Where can you get a job after learning SQL:
When you learn skills like SQL and database, you can work in many different industries. Below are some main sectors where SQL is used a lot:
- IT and software development: Here SQL is used to create and manage databases in web apps, mobile apps and software of big companies.
- Finance and Fintech: Fast and secure databases are created for banking, trading platforms and online payment systems. SQL is very important here.
- E-commerce and retail: Sites like Amazon, Flipkart – they have data of millions of products, customers and orders. Everything is managed with SQL.
- Healthcare and medical field: Databases are designed to store patient records, clinical trial data, medical research etc.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics: Here data warehouses and data marts are created so that the company can do its reports and analysis. All the data is prepared using SQL.
- Gaming Industry: SQL databases are used to handle all the data like player profiles, game scores, in-game purchases, etc.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Inventory of goods, shipment, and the entire supply chain data is tracked in SQL databases. This ensures that everything reaches on time.
- Government and Public Sector: Databases are created to keep census, public service records, government schemes data – everything in a good order.